Stages Of Cannabis Growth And Needs
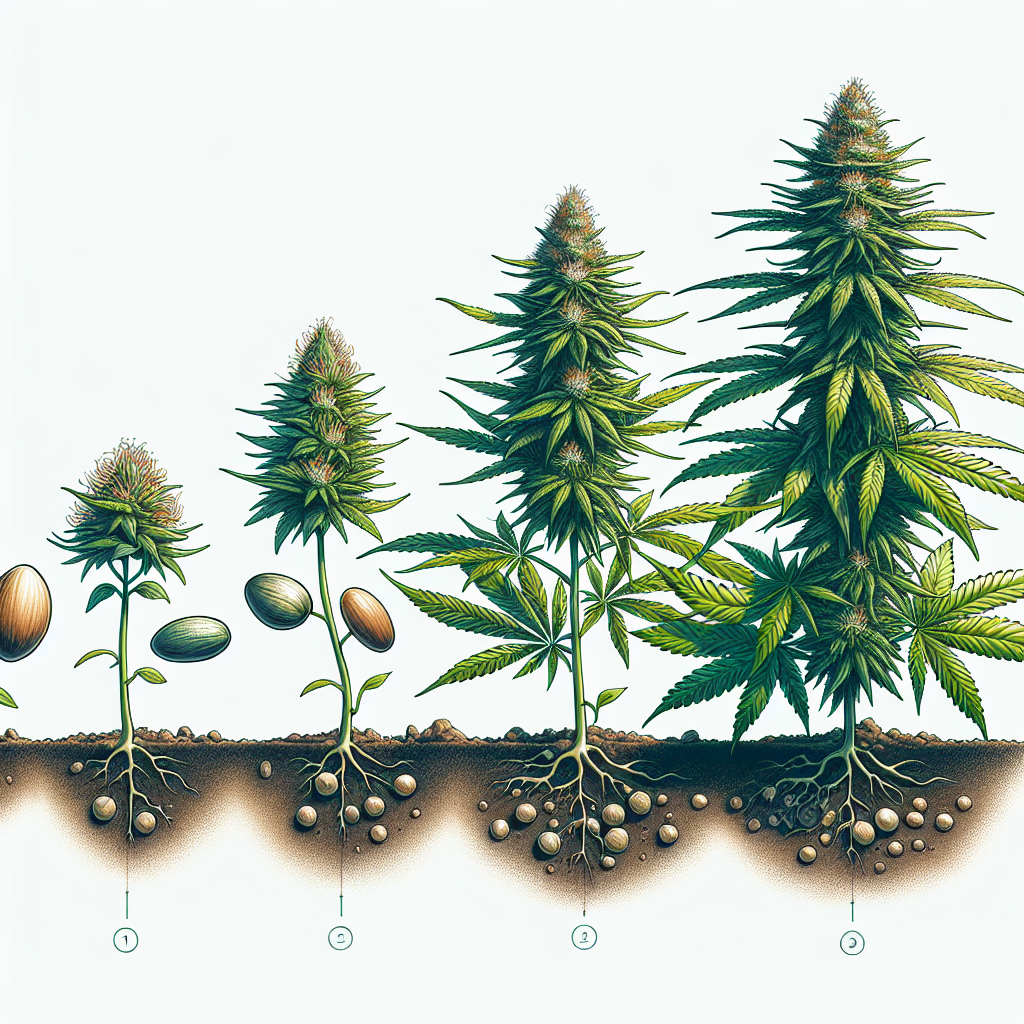
Stages Of Cannabis Growth And Needs. Are you interested in cultivating your own cannabis? Understanding the various stages of cannabis growth and their corresponding needs is essential for a successful harvest. From the germination stage to the flowering stage, each phase requires specific care and attention to ensure optimal growth and maximize your yield. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced grower, this article will guide you through the different stages of cannabis growth and provide you with valuable tips to nurture your plants every step of the way. So, grab your gardening tools and get ready to embark on a rewarding journey of cannabis cultivation!
Seed Germination
Factors Influencing Germination
Germination is a crucial stage in the life cycle of a cannabis plant. Several factors play a significant role in determining whether the seeds will successfully germinate or not. The most important factor is moisture. Seeds require adequate moisture to activate enzymes responsible for germination. Temperature is another crucial factor that affects germination. Cannabis seeds typically germinate best at temperatures between 20-30 degrees Celsius (68-86 degree Fahrenheit). Additionally, light exposure can also influence germination, with some cannabis seeds preferring darkness for successful sprouting.
Steps for Successful Germination
To ensure successful germination, it is essential to follow a few key steps. First, start by soaking the seeds in water for 24 hours, which softens the seed coat and encourages the germination process. After soaking, transfer the seeds to a moist medium such as a damp paper towel or peat pellet. Keep the medium consistently moist but avoid over-watering to prevent fungal growth. It is also crucial to maintain the ideal temperature and darkness or light conditions, depending on the specific needs of the seeds. With proper care and attention to these steps, you can increase the chances of successful seed germination.
Seedling Stage
Ideal Growing Environment
The seedling stage is a critical phase where the tiny sprouts develop into young cannabis plants. Providing an ideal growing environment during this stage sets the foundation for a healthy and vigorous plant. Firstly, ensure that the seedlings receive ample light. A grow light with a spectrum suitable for vegetative growth is recommended. Secondly, maintain the temperature in the range of 20-25 degrees Celsius (68-77 degrees Fahrenheit) to promote optimal growth. Additionally, it is important to maintain humidity levels between 70% and 80% to prevent the seedlings from drying out.
Light and Temperature Requirements
During the seedling stage, young cannabis plants require about 18 hours of light per day. This extended light period mimics long summer days and promotes vegetative growth. Providing a consistent light source is crucial for healthy development. In terms of temperature, seedlings thrive in a range of 20-25 degrees Celsius (68-77 degrees Fahrenheit). Lower temperatures might slow down growth, while higher temperatures can lead to stress and stunted development. It is essential to monitor and maintain these light and temperature requirements to ensure optimal growth during the seedling stage.
Watering and Nutrient Needs
Proper watering is crucial during the seedling stage. Seedlings have delicate roots that require moisture but are also susceptible to over-watering. Water the young plants gently, allowing the soil to dry slightly between waterings to prevent root rot. Additionally, it is important to use a well-draining growing medium to prevent excess water retention. As for nutrients, seedlings typically have enough nutrients stored in the seed to support their initial growth. Avoid over-fertilizing during this stage, as it can lead to nutrient burn and hinder the seedling’s development. Focus on providing a balanced and gentle approach to watering and nutrient care for healthy seedling growth.
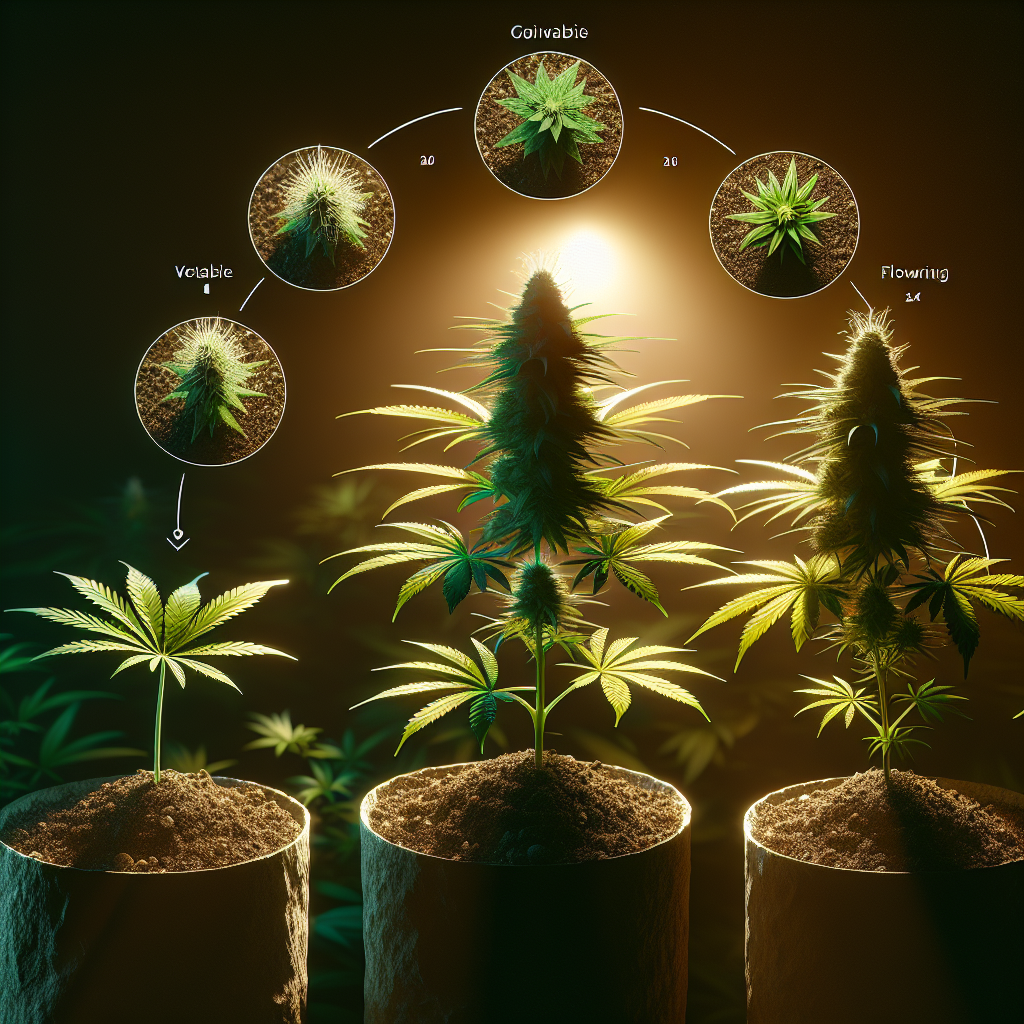

Vegetative Stage
Duration of Vegetative Stage
The vegetative stage is a crucial period where cannabis plants focus on creating a strong structure before transitioning to the flowering stage. The duration of this stage varies depending on various factors, such as the strain and desired plant size. Typically, the vegetative stage lasts around 4-8 weeks, but some growers may extend it to allow for larger plants. Monitoring plant height, overall size, and the desired yield can help determine the ideal duration of the vegetative stage for your specific needs.
Light Cycle Considerations
Light cycles play a significant role in the vegetative stage of cannabis growth. During this stage, it is recommended to provide a light cycle of 18-24 hours of light per day. The extended light period allows the plant to focus on leaf and stem development, promoting vigorous growth. Many growers opt for 18 hours of light per day as it strikes a balance between energy consumption and growth efficiency. However, some strains may benefit from longer light cycles, reaching up to 24 hours per day. It is crucial to research the specific needs of your chosen strain to optimize growth during the vegetative stage.
Nutrient Requirements
Cannabis plants in the vegetative stage have specific nutrient requirements to support healthy growth. Nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) are essential macronutrients required in higher concentrations during this stage. Nitrogen supports leaf and stem development, while phosphorus and potassium aid in root development and overall plant structure. It is crucial to provide a balanced and complete fertilizer formulated specifically for the vegetative stage. However, avoid excessive nitrogen levels as it can lead to nutrient burn and hinder growth. Regularly monitor and adjust nutrient levels to ensure optimal nutrient uptake for healthy vegetative growth.
Pruning and Training
Methods for Pruning and Training
Pruning and training techniques are vital for shaping and maximizing cannabis plant growth. Pruning involves strategically removing certain parts of the plant, such as lower leaves, to promote better airflow and light penetration. Training, on the other hand, involves manipulating the plant’s growth patterns to achieve a desired shape or increase bud production. Common methods of pruning include defoliating lower leaves, removing sucker shoots, and trimming excessive growth. Training techniques include topping, where the main stem is trimmed to encourage lateral growth, and low-stress training (LST), where branches are gently bent and secured to promote even canopy development.
Benefits of Pruning and Training
Pruning and training techniques offer several benefits for cannabis cultivation. By removing lower leaves and excess growth, pruning improves airflow and light penetration throughout the plant. This reduces the risk of mold and pests while promoting stronger and healthier plant growth. Training techniques allow for a more even and efficient use of available light, resulting in increased bud production and yields. The manipulation of growth patterns also helps create a canopy with consistent bud development and reduces the need for excessive support structures. Overall, pruning and training techniques can significantly improve the quality and quantity of your cannabis harvest.
Common Techniques
Some commonly used techniques for pruning and training cannabis plants include topping, FIMming, and low-stress training (LST). Topping involves removing the main stem’s apical bud, which encourages the growth of multiple lateral branches. FIMming is a similar technique where the apical bud is trimmed partially instead of removing it entirely. This method promotes the growth of multiple main colas while minimizing stress on the plant. Low-stress training (LST) involves gently bending and securing branches to encourage lateral growth and create an even canopy. These techniques are widely used by growers to shape cannabis plants and maximize bud production.
Flowering Stage
Transition to Flowering
The flowering stage is an exciting phase where cannabis plants start producing buds. To initiate flowering, a change in light cycle is required. Cannabis plants require a consistent 12 hours of uninterrupted darkness to trigger flowering. This mimics the natural light changes that occur during the autumn season, signaling the plant to start focusing on reproductive growth. It is crucial to maintain this uninterrupted period of darkness throughout the flowering stage to prevent any interruption in the plant’s flowering process.
Environmental Factors Affecting Flowering
Several environmental factors can affect the flowering stage of cannabis plants. Temperature plays a significant role, with most strains performing best in a range of 20-26 degrees Celsius (68-79 degrees Fahrenheit). Consistent temperature control helps optimize bud development and resin production. Additionally, humidity levels should be carefully monitored during this stage, as high humidity can increase the risk of mold and mildew. Proper airflow and ventilation are crucial to prevent these issues. It is also important to avoid excessive fluctuations in light intensity, as it can stress the plants and affect bud development.
Bud Development
Bud development is the primary focus during the flowering stage of cannabis growth. The buds are the precious flowers that contain the cannabinoids and terpenes responsible for the plant’s unique properties. As the plants enter the flowering stage, small clusters of flowers, known as bud sites, start to form. These bud sites will gradually grow and swell, becoming dense and resinous. Proper care and maintenance during this stage, such as nutrient management and pest control, are essential to support healthy bud development. The length of the flowering stage varies depending on the strain, typically ranging from 6-12 weeks.
Male vs Female Plants
Differentiating Male and Female Plants
In cannabis cultivation, it is important to differentiate between male and female plants. Female plants produce the buds that are sought after for their recreational or medicinal properties, while male plants produce pollen for fertilization. Male plants are identifiable by their pollen sacs, which contain the pollen needed for reproduction. On the other hand, female plants have stigma, which catches pollen to begin seed development. To prevent unintentional pollination and seed production, it is crucial to promptly identify and remove male plants from the growing area.
Implications for Cannabis Cultivation
Understanding the difference between male and female plants is essential for cannabis cultivation. For those growing cannabis for buds, keeping only female plants is crucial to ensure a high-quality and seedless harvest. Male plants should be removed as soon as they are identified to prevent any accidental fertilization, which would result in the formation of seeds and a decrease in bud quality and potency. By strictly maintaining a female-only garden, growers can focus their resources on growing high-quality buds and maximizing their yield.
Harvesting and Drying
Signs of Harvest Readiness
Harvesting cannabis at the right time is crucial to maximize potency, flavor, and overall quality. Several signs can indicate that your cannabis plants are ready for harvest. One of the most noticeable signs is the change in trichome color. Trichomes are the tiny, resinous structures that cover the buds. As harvest time approaches, the trichomes change from translucent to a milky white or amber color. Additionally, the pistils (hairs) on the buds will change color from white to a reddish-brown or orange hue. Monitoring these signs and observing the overall development of the buds will help determine the optimal time to harvest.
Methods of Harvesting
Once your cannabis plants are ready for harvest, there are different methods you can use to harvest the buds. One common method is cutting the entire plant at the base and hanging it upside down in a cool, dark, and well-ventilated space to dry. This method, known as dry trimming, allows the plant to slowly dry, preserving the flavors and aromas of the buds. Alternatively, you can choose to trim the buds off the plant immediately after cutting. This method, known as wet trimming, speeds up the drying process but may result in a slightly different flavor profile. Both methods have their advantages, and the choice depends on personal preference and drying conditions.
Importance of Proper Drying
Proper drying is crucial to preserve the quality, potency, and flavor of harvested cannabis. After harvesting, the buds need to dry slowly in a dark and well-ventilated space with low humidity. The drying process helps remove excess moisture from the buds while allowing them to retain their desired cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavors. Drying too quickly can result in harsh and undesirable flavors, while drying too slowly can lead to mold or mildew growth. It is important to monitor the drying environment regularly and make adjustments as needed to ensure a slow and controlled drying process that will yield high-quality dried cannabis.
Curing and Storage
Purpose of Curing
Curing is a crucial step that follows the drying process and involves storing dried cannabis buds in a controlled environment. The purpose of curing is to further enhance the flavors, aromas, and quality of the buds. During the curing process, the remaining moisture inside the buds redistributes evenly, resulting in a smoother smoke and improved taste. Curing also helps break down chlorophyll and other compounds, which can contribute to a harsh taste if not properly cured. The overall result of a well-cured cannabis is a more enjoyable and refined smoking experience.
Curing Process
To properly cure cannabis, begin by placing the dried buds in airtight containers, such as glass jars. This ensures an airtight environment that allows the buds to slowly release excess moisture while retaining their desirable qualities. During the first few days, it is important to open the jars for a few minutes each day to release any built-up humidity. This process, known as burping, helps prevent mold and mildew growth. Over the course of several weeks, continue to burp the jars less frequently until the desired level of moisture is reached. Regularly monitoring the buds’ moisture content during the curing process ensures a well-cured and flavorful final product.
Storage Considerations
Proper storage is essential to maintain the freshness and quality of cured cannabis. Once the buds have been cured, store them in a cool, dark, and dry place to preserve their potency and flavors. Light and heat can degrade cannabinoids and terpenes, leading to decreased potency and aroma. It is recommended to use airtight glass containers, such as Mason jars, to store the cured buds, as they provide a secure and stable environment. Avoid plastic bags or containers, as they can create an unfavorable environment and may lead to mold or mildew growth. By following these storage considerations, you can ensure long-lasting and enjoyable cannabis products.
Pest and Disease Management
Common Cannabis Pests
While growing cannabis, it is important to be aware of common pests that can infest and damage the plants. Some of the most common pests that affect cannabis cultivation include spider mites, aphids, whiteflies, and thrips. These pests can suck the sap from the plant, weaken its structure, and introduce diseases. Recognizing the signs of infestation, such as leaf discoloration, webbing, or visible insects, is crucial to prompt identification and treatment.
Preventive Measures
Preventing pest infestations is essential for successful cannabis cultivation. Start by maintaining a clean and hygienic growing environment, as pests are attracted to debris and dead plant material. Regularly inspect the plants for signs of pests and promptly remove any affected areas. Introducing beneficial insects, such as ladybugs or predatory mites, can also help control pests naturally. Additionally, implementing proper sanitation practices, including cleaning tools and equipment, can prevent the spread of pests within the grow area.
Treatment Options
If an infestation occurs, it is important to take immediate action to prevent further damage. Treatment options vary depending on the specific pests and the severity of the infestation. Organic insecticidal soaps or oils can be effective in controlling small infestations, as they suffocate and disrupt the pests’ life cycle. However, for larger infestations or more resilient pests, chemical insecticides may be necessary. It is crucial to carefully follow instructions and dosage recommendations when using chemical solutions and to consider their potential impacts on the environment and human health. Consulting with a reputable pest management professional can provide guidance and ensure safe and effective treatment.
Nutrient and Watering Needs
Essential Cannabis Nutrients
Cannabis plants have specific nutrient requirements to support healthy growth and development. The primary macronutrients required by cannabis are nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K). Nitrogen promotes leaf and stem growth, phosphorus supports root development and overall plant structure, and potassium aids in flowering and bud production. Additionally, secondary macronutrients, such as calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), and sulfur (S), are also vital for optimal plant health. Micronutrients, including iron (Fe), zinc (Zn), manganese (Mn), and others, are required in smaller quantities but are equally essential for healthy growth.
Feeding Schedule
Establishing a regular feeding schedule is crucial to ensure the plants receive the necessary nutrients at the appropriate stages of growth. During the seedling and vegetative stages, nitrogen-rich fertilizers are typically used to support vigorous leaf and stem development. As the plants transition to the flowering stage, a shift towards phosphorus and potassium-rich fertilizers helps promote bud development. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for dosage and frequency when applying fertilizers. Regularly monitoring the plants’ response to the feeding schedule and making adjustments as needed will help maintain optimal nutrient levels throughout the growth cycle.
Importance of pH Level
Maintaining the appropriate pH level in the growing medium is vital for nutrient uptake and overall plant health. Cannabis plants thrive in slightly acidic to neutral pH levels, typically ranging from 6.0 to 7.0. When the pH deviates too far from this range, nutrient deficiencies or toxicities can occur, resulting in stunted growth and poor plant health. Testing the pH of the soil or growing medium regularly and adjusting it when necessary ensures that the plants can effectively absorb the available nutrients. pH adjusters, such as pH-Up or pH-Down solutions, can be used to bring the pH within the desired range. By monitoring and maintaining the pH level, you can optimize nutrient availability and support healthy cannabis growth.
Thanks for checking out my
Stages Of Cannabis Growth And Needs
If you need any seeds or more info click the button below:










